Antitussives (Latin Tussis- cough) are the agents which act upon the pulmonary membrane that hasten or alter expectoration. These stimulate and expel the bronchial mucous or secretions and help in their removal.
Monday, August 6, 2018
Sunday, August 5, 2018
 6:21 AM
6:21 AM SANA BASRI PATEL
SANA BASRI PATEL AYURVEDA
AYURVEDA No comments
No comments
ANTI TUMOR DRUGS
Antitumour (Latin : Tumor swelling, neoplasm) drugs are used in the treatment of cancer. The cancer or carcinogenic growth is an abnormal mass of new tissue growing in or on part of the body. Several types of carcinogenic growths have been reported. The cancer is regarded to be an incurable disease in secondary stages. The radioactive substances, metal compounds and several chemotherapeutic drugs have been suggested to control the carcinogenic growths.
The promising natural antitumour drugs or their isolates are obtained from the following:
Vinca : (Catharanthus roseus) Podophyllum : (Podophyllum hexandrum)
Colchicum : (Colchicum Iuteum) Benafsha : (Viola odorata)
Anacardium : (Semecarpus anacardium)
VlNCA
Synonyms : Catharanthus, Vinca rosea, Periwinkle
Biological Source: It is the dried whole plant of Catharanthus roseus 'G. Don., (syn vinca-roseai (Family : Apocynaceae).
Geographical Distribution:
It is probably indigenous to Madagascar. It is cultivated in South Africa, West indies, lndia, U.S.A., Europe and Australia as an ornamental plant, as well as, for its medicinal properties.
Organoleptic Characters (Fig) :
The leaves are green, roots are pale grey, flowers are violet, pink-white or carmine-red in colour. The odour is characteristic and taste is bitter. Vinca is an erect, pubescent herb, with branched tap-root. Leaves are simple, petiolate, ovate, or oblong, unicostate, reticulate, entire, brittle with acute apex and glossy appearance. Flowers are bractate,pedicellate, complete, hermaphrodite, normally 2 to 3 in cymose axillary clusters. Fruits are follicles with several black seeds.
Chemical Constituents :
Vinca contains wide varieties of chemicals including the glycosides and alkaloids. The indole~indoline alkaloids are very important constituents. About 60 alkaloids have been isolated so far from different parts of vinca. The important alkaloids with anticancer property are vincristine and vinblastine. Vincristine is obtained in about 0.0002 % yield from the crude drug. The other alkaloids present in the drug are ajmalicine, serpentine, lochnerine and tetrahydroalstonine. The total alkaloidal content of the drug is about 1 %, of which only a fraction contains therapeutically active alkaloids.
Both vinblastine and vincristine have the same structures with the difference that in vinblastine there is N-methyl group while, in vincristine it is N-formyl group and both Possess different activities. The other alkaloids are vindoline, vindolinine and catharanthine.
Uses:
Vincristine is used in treatment of leukaemia. Vinblastine is used for the treatment of generalised Hodgkin's disease and chorionepithelioma. Vinca also exhibits hypotensive and antidiabetic activity.
Antitumour (Latin : Tumor swelling, neoplasm) drugs are used in the treatment of cancer. The cancer or carcinogenic growth is an abnormal mass of new tissue growing in or on part of the body. Several types of carcinogenic growths have been reported. The cancer is regarded to be an incurable disease in secondary stages. The radioactive substances, metal compounds and several chemotherapeutic drugs have been suggested to control the carcinogenic growths.
The promising natural antitumour drugs or their isolates are obtained from the following:
Vinca : (Catharanthus roseus) Podophyllum : (Podophyllum hexandrum)
Colchicum : (Colchicum Iuteum) Benafsha : (Viola odorata)
Anacardium : (Semecarpus anacardium)
VlNCA
Synonyms : Catharanthus, Vinca rosea, Periwinkle
Biological Source: It is the dried whole plant of Catharanthus roseus 'G. Don., (syn vinca-roseai (Family : Apocynaceae).
Geographical Distribution:
It is probably indigenous to Madagascar. It is cultivated in South Africa, West indies, lndia, U.S.A., Europe and Australia as an ornamental plant, as well as, for its medicinal properties.
Organoleptic Characters (Fig) :
The leaves are green, roots are pale grey, flowers are violet, pink-white or carmine-red in colour. The odour is characteristic and taste is bitter. Vinca is an erect, pubescent herb, with branched tap-root. Leaves are simple, petiolate, ovate, or oblong, unicostate, reticulate, entire, brittle with acute apex and glossy appearance. Flowers are bractate,pedicellate, complete, hermaphrodite, normally 2 to 3 in cymose axillary clusters. Fruits are follicles with several black seeds.
 |
| VINCA ROSEA |
 |
| VINCA FLOWER |
Chemical Constituents :
Vinca contains wide varieties of chemicals including the glycosides and alkaloids. The indole~indoline alkaloids are very important constituents. About 60 alkaloids have been isolated so far from different parts of vinca. The important alkaloids with anticancer property are vincristine and vinblastine. Vincristine is obtained in about 0.0002 % yield from the crude drug. The other alkaloids present in the drug are ajmalicine, serpentine, lochnerine and tetrahydroalstonine. The total alkaloidal content of the drug is about 1 %, of which only a fraction contains therapeutically active alkaloids.
Both vinblastine and vincristine have the same structures with the difference that in vinblastine there is N-methyl group while, in vincristine it is N-formyl group and both Possess different activities. The other alkaloids are vindoline, vindolinine and catharanthine.
Uses:
Vincristine is used in treatment of leukaemia. Vinblastine is used for the treatment of generalised Hodgkin's disease and chorionepithelioma. Vinca also exhibits hypotensive and antidiabetic activity.
Saturday, August 4, 2018
 9:21 AM
9:21 AM SANA BASRI PATEL
SANA BASRI PATEL AYURVEDA
AYURVEDA 2 comments
2 comments
GINGER
Ginger consists of rhizomes of Zingiber officinale Roscoe, Family : Zingiberaceae, scrapped to remove outer skin and dried in sun. It contains not less than 0.8% of total gingerols on dried basis.
Geographical Distribution :
it is said to be native of South East Asia, but is cultivated in West Indies, Africa, Australia, Mauritius, Jamaica, Taiwan and India. More than 50 % of the world's
production is from lndia.
Organoleptic Characters
Colour : Externally, it is buff coloured,
Odour : Aggreeable and aromatic.
Taste : Aggreeable and pungent. Size : Rhizomes of ginger are about 5 to 15 x 1.5 to 6.5 cm.
Shape : Rhizomes are laterally compressed bearing short flat, ovate and oblique branches on the upper side, with bud at the apex.
Fracture '. Short and fibrous.
Uses :
Ginger is used as a stomachic, an aromatic, a carminative, stimulant and flavouring agent. Ginger oil is used in mouth washes, ginger-beverages and liquors.
Synonyms : Zingiber; Zingiberis, Sonth ,
Biological Source :Ginger consists of rhizomes of Zingiber officinale Roscoe, Family : Zingiberaceae, scrapped to remove outer skin and dried in sun. It contains not less than 0.8% of total gingerols on dried basis.
Geographical Distribution :
it is said to be native of South East Asia, but is cultivated in West Indies, Africa, Australia, Mauritius, Jamaica, Taiwan and India. More than 50 % of the world's
production is from lndia.
Organoleptic Characters
Colour : Externally, it is buff coloured,
Odour : Aggreeable and aromatic.
Taste : Aggreeable and pungent. Size : Rhizomes of ginger are about 5 to 15 x 1.5 to 6.5 cm.
Shape : Rhizomes are laterally compressed bearing short flat, ovate and oblique branches on the upper side, with bud at the apex.
 |
| T.S OF GINGER |
 |
| ZINGER OFFICINALE |
Fracture '. Short and fibrous.
Uses :
Ginger is used as a stomachic, an aromatic, a carminative, stimulant and flavouring agent. Ginger oil is used in mouth washes, ginger-beverages and liquors.
Friday, August 3, 2018
 10:25 AM
10:25 AM SANA BASRI PATEL
SANA BASRI PATEL AYURVEDA
AYURVEDA 3 comments
3 comments
FENNEL
Synonyms: Fennel fruits, Fructus Foeniculum, Saunf
Biological Source: Fennel consists of dried ripe fruits of the plant known as Foeniculum vulgare Miller(Family : Umbelliferae) obtained by cultivation. It should contain not less than 1.4 % of volatile oil.
Geographical Distribution : It is indigenous to Mediterranean countries and largely cultivated in Rumania, Russia, Germany, France, India and Japan.In India it is cultivated in Gujarat, Punjab, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal.
Organoleptic Characters : Colour : Green to yellowish-brown.
Odour : Sweet aromatic.
Taste : Strongly aromatic and mucilaginous.
Size : 5 to 10x 2 to 4mtn.
Shape : Straight or slightly curved
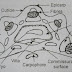
T.S of mericarp of fennel
Chemical Constituents : Fennel consists of 3 to 7 % of volatile oil about 20% each of proteins and fixed oil. The chief active constituent of volatile oil is a ketone, fenchone (about 20%) and a phenolic ether, anethole (about 50 %). The other constituents are phellandrene, Limonene, methyl chavicol, anisic aldehyde etc. Fenchone is a colourless liquid with pungent odour. The anethole is sweet in odour and taste.
Uses :
It is used as a carminative, an aromatic and a stimulant. It is also an expectorant. Pharmaceutically it is used as a flavouring agent.
 9:46 AM
9:46 AM SANA BASRI PATEL
SANA BASRI PATEL AYURVEDA
AYURVEDA No comments
No comments
CINNAMON
Synonyms: Cinnamon bark; Kalmi-Dalchini, Ceylon cinnamon
Biological Source :
Cinnamon consists of dried inner bark of shoots of coppiced trees of Cinnamomum zeylanicum Nees belonging to family Lauraceae. lt should not contain less than 1.0 % of volatile oil.
Cinnamon consists of dried inner bark of shoots of coppiced trees of Cinnamomum zeylanicum Nees belonging to family Lauraceae. lt should not contain less than 1.0 % of volatile oil.
Geographical Distribution :
Cinnamon, the evergreen tree of tropical area is considered to be native of Sri Lanka and Malabar coast of lndia. lt is also found in Jamaica and Brazil. However, most of the world requirements are met by Sri Lanka and hence true cinnamon is known as I Ceylon cinnamon.Chemical Test:
On addition of a drop of ferric chloride solution to a drop of volatile oil, a pale green colour is produced. With ferric chloride, cinnamic aldehyde gives brown colour and eugenol gives blue colour, resulting in formation of pale green colour.
in cassia oil, brown colour is obtained, as it contains only cinnamic aldehyde .
Uses:
Bark is used as a carminative, stomachic and mild astringent. It is also used as a flavouring agent, stimulant, an aromatic and antiseptic. Commercially, it is used as a spice and condiment, and also in the preparation of candy, dentifrices and perfumes.
Colour : The outer surface is dull yellowish-brown, while the inner surface is dark yellowish-brown.
Odour : Aromatic, sweet followed by warm sensation.
Taste : Found in the form of compound quills. . ,
Size : About 1 m in length and 1 cm in diameter. The thickness of the bark is approximately 0.5 mm.
Fracture : Splintery.
Fracture : Splintery.
 |
| CINNAMON STICK |
 |
| CINNAMON LEAF |
Chemical Constituents :
Cinnamon bark contains about 0.5 to 1.0 % of volatile oil, 1.2 % of tannins
(phlobatanmns), mucilage, calcium oxalate, starch and a sweet substance known as mannitol. .
Bark yields 14 -16 % of 90 % alcohol-soluble extractives.
The volatile oil is the active constituent of the drug. lt is light yellow (when freshly distilled) in colour and changes to red on storage.
Cinnamon oil contains 60 7O % cinnamaldehyde, 5 10 % eugenol, benzaldehyde, cuminaldehyde and other terpenes like phellandrene, pinene, cymene, caryophyllane etc.
Chemical Test:
On addition of a drop of ferric chloride solution to a drop of volatile oil, a pale green colour is produced. With ferric chloride, cinnamic aldehyde gives brown colour and eugenol gives blue colour, resulting in formation of pale green colour.
in cassia oil, brown colour is obtained, as it contains only cinnamic aldehyde .
Uses:
Bark is used as a carminatiye, stomachic and mild astringent. It is also used as a flavouring agent, stimulant, an aromatic and antiseptic. Commercially, it is used as a spice and condiment, and also in the preparation of candy, dentifrices and perfumes.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)